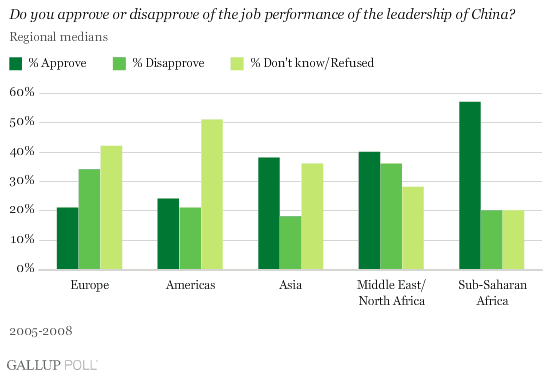
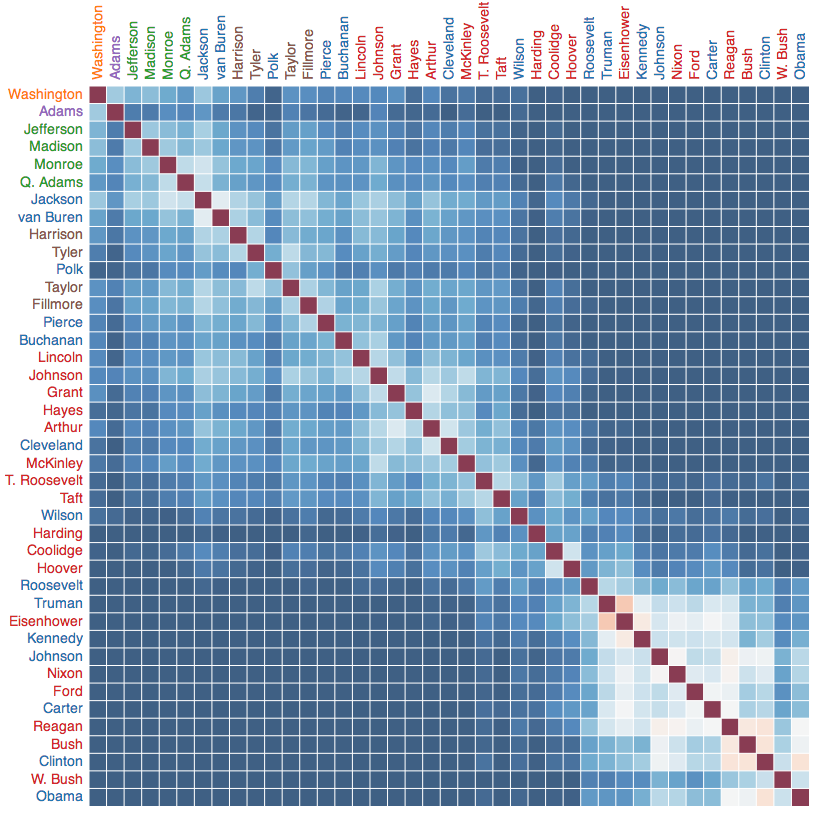
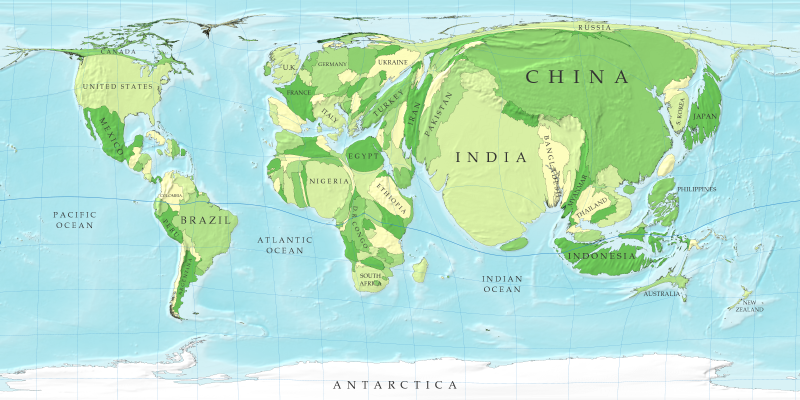
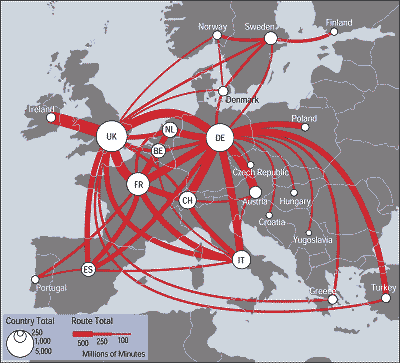
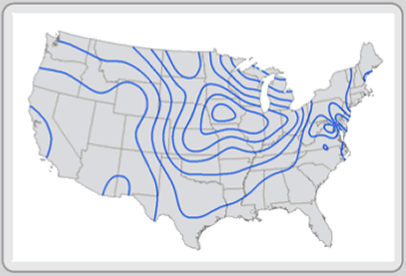
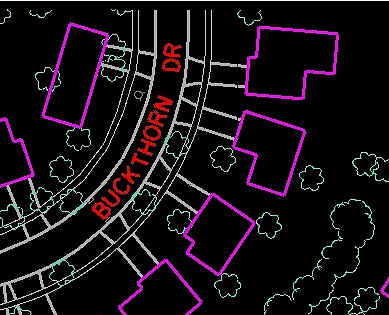
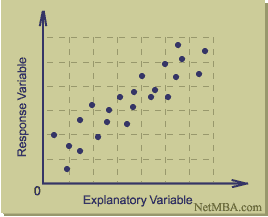
http://eps.mq.edu.au/courses/GEOS219/choropleth.htm
Unstandardized choropleth maps can be determined by whether or not a map is areally averaged. They don't average or standardize the data. This example of an unstandardized choropleth map exhibits deaths of babies every 1,000 live births in Australia. The legend classes from bottom to top read: suppressed, less than 5, 5-6, 6-7, 7-10, 10 or more.